Are you tired of seeing perfectly good food go to waste? Did you know that almost one-third of all food produced worldwide is wasted annually? This blog post will explain sustainable food waste management and its importance in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving resources.
Let’s explore how you can make a difference starting right at home. Keep reading!
Key Takeaways
- Almost one-third of all food produced globally is wasted each year. Efficient food waste management involves strategies like donation, composting, and upcycling to reduce this waste.
- Proper segmentation of organic waste reduces landfill contributions and helps convert discarded food into useful resources such as biogas or compost, which enrich soil and reduce methane emissions.
- Sustainable practices at home include setting up a compost bin for kitchen scraps, meal planning to avoid extra purchases, portion control to decrease plate waste, and using airtight containers to extend perishable items’ shelf life.
- Government initiatives provide support through policies that promote reduction efforts. Campaigns like “Love Food Hate Waste” educate the public on effective ways to minimise food loss.
- The Covid-19 pandemic increased household food wastage due to panic buying and stockpiling. Proper meal planning skills can help manage groceries more efficiently during such disruptions.
What is Sustainable Food Waste Management?
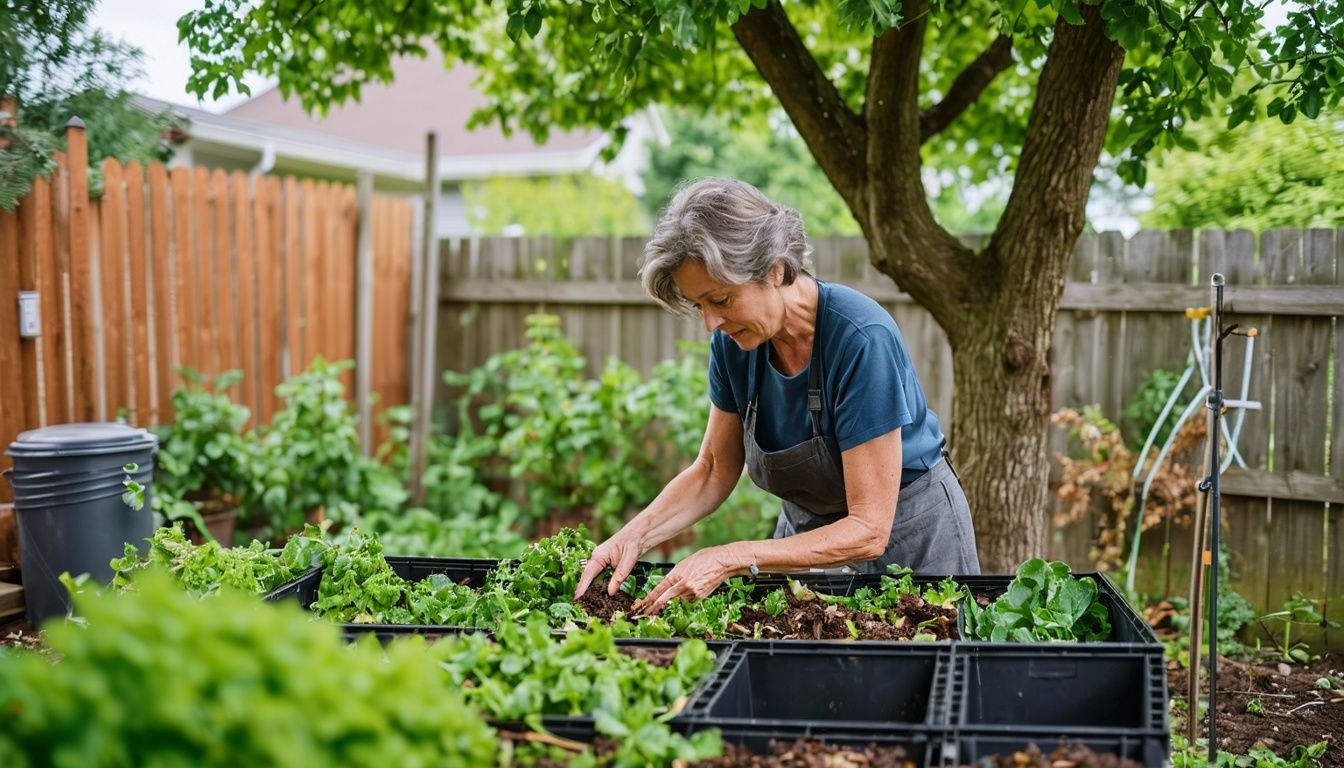 Sustainable food waste management means handling discarded food in ways that protect our environment. It reduces waste and turns leftovers into useful resources like compost or biogas.
Sustainable food waste management means handling discarded food in ways that protect our environment. It reduces waste and turns leftovers into useful resources like compost or biogas.
Definition and basics
Food waste management involves strategies to reduce, reuse, and recycle food discards. This practice aims to minimise environmental impact. Proper segmentation of organic waste is vital for efficient processing.
Methods such as donation, upcycling, and composting play key roles. Donating excess food helps those in need while decreasing waste in landfills. Composting converts organic matter into useful manure, enriching soils and reducing methane emissions from landfilled waste.
Importance of proper management
Efficient food waste management is vital for safeguarding our environment and resources. Proper practices minimise environmental impact by reducing landfill waste, conserving natural resources, and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
For instance, anaerobic digestion transforms organic matter into biogas and fertilisers, supporting a circular economy.
“Reducing food losses and waste helps address global hunger,” says the World Resources Institute (WRI).
Segmentation of waste ensures proper disposal methods like composting or donation to those in need. This prevents usable food from becoming garbage. Effective inventory practices in the food industry reduce overproduction that leads to wastage.
Sustainable development goal target 12.3 aims to halve per capita global food loss by 2030—highlighting the importance of managing wasted goods properly.
Methods of managing food waste (e.g. donation, upcycling, composting, etc.)
Proper food waste management is vital to ensuring minimal environmental impact. Understanding different methods can help reduce wasted food and its associated issues.
- Food Donation: Redirecting surplus food to those in need helps fight hunger. Organisations like FareShare in the UK distribute excess food from retailers and manufacturers to charities, feeding thousands of people.
- Upcycling: Transforming food by-products into new and useful products reduces waste. For example, using orange peels for cleaning solutions or animal feed maximises resources and decreases landfill waste.
- Composting: Converting organic waste into compost enriches soil without chemical fertilisers. Home composting bins decompose kitchen scraps into valuable nutrients, improving garden health and reducing landfill contributions.
- Anaerobic Digestion: This process breaks down food waste to produce biogas as a renewable energy source. The method also creates digestate, which serves as a high-quality fertiliser, closing the loop in sustainable food systems.
- Recycling: Separating recyclables such as packaging materials from organic waste reduces overall trash volume. Proper segmentation allows for better recycling processes and efficient use of resources.
- Incineration with Energy Recovery: Burning non-recyclable waste at high temperatures generates electricity or heat, minimising landfill usage while producing energy.
- Government Support: Initiatives like “Love Food Hate Waste” campaigns encourage households to plan better and prevent food loss and waste through education and practical tips.
- Retailer Practices: Supermarkets can adopt practices like dynamic pricing for near-expiry products or donating unsold goods to charities, significantly cutting down on wasted food.
- Educational Programmes: Schools can teach children essential skills for planning meals and cost management, nurturing a new generation that values sustainable habits.
- Community Projects: Local projects like community gardens use upcycled or donated seeds and compost from neighbourhood food scraps, promoting sustainability at the grassroot level.
Implementing these methods collectively addresses climate change by reducing carbon dioxide emissions and other greenhouse gases from decomposing wastes in landfills or coal-fired power plants from incineration without recovery benefits.
Impact of Food Waste on the Environment
Food waste contributes significantly to carbon dioxide emissions. It also consumes vital resources like water and energy needed for food production.
Greenhouse gas emissions
Rotting food in landfills emits a lot of methane. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, even more harmful than carbon dioxide. This contributes significantly to global warming.
Proper management such as composting can reduce these emissions. It helps waste decompose without releasing harmful gases. Sustainable food waste management helps address climate change and conserve resources like water and energy used in food production.
Resource conservation
Food waste not only produces greenhouse gases but also wastes important resources. Each wasted item represents water, energy, and labour used in farming, transportation, storage, and cooking.
This is why resource conservation is crucial.
Reducing food wastage means conserving valuable resources that could support sustainable development goals. Efficient inventory management in restaurants and homes helps cut down food losses across the supply chain.
By doing this, we save precious water supplies and lower carbon dioxide emissions from production processes. It also frees up land for other uses like energy crops or nature reserves rather than landfill sites filled with decomposing waste.
Benefits of Sustainable Food Waste Management
Sustainable food waste management helps reduce the amount of garbage in landfills. It also supports the economy by saving money and resources.
Helping those in need
Food waste hampers efforts to fight global hunger. Redistributing surplus food can help feed the undernourished. Many organisations, like NGOs, play a key role in this process. They collect excess food from supermarkets and restaurants and deliver it to those who need it most.
The practice of food redistribution not only aids in alleviating hunger but also reduces landfill waste. For example, FareShare, an NGO in the UK, redistributes millions of meals annually.
This benefits both the environment and society by lowering greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing wasted foods while supporting food-insecure communities.
Economic savings
Reducing food waste helps those in need and also saves money. Households, restaurants, and even large corporations can benefit from efficient food management. Proper planning reduces expenses on unnecessary purchases.
Using a compost bin lowers the cost of waste disposal services. This not only cuts down landfill fees but also enriches soil for gardens or farms. The less discarded food means fewer resources wasted throughout the supply chain.
Efficient inventory management is key in reducing costs and preventing food loss.
Reduction of waste in landfills
Reducing waste in landfills is crucial for lowering methane emissions. This greenhouse gas results from decomposing organic matter. Proper food waste management can divert significant amounts of waste from landfills.
Composting at home serves as an effective method to recycle garden and kitchen scraps into nutrient-rich soil.
Donation and upcycling also play a vital role in this process. Restaurants, supermarkets, and individuals can redirect surplus food to those in need. Efficient inventory management reduces food losses along the supply chain, which saves resources and cuts down on transportation costs related to landfill use.
Government initiatives support these efforts by providing guidelines and incentives for sustainable practices.
How to Reduce and Recycle Food Waste
Compost kitchen scraps in your garden. Use leftovers creatively to make new meals. Support local food recycling programs.
1. At home (e.g. composting, recycling)
Managing food waste at home is crucial for a sustainable future. Simple steps can make a big difference in waste reduction and recycling.
- Composting:
- Set up a compost bin in your garden.
- Use food scraps like fruit peels, vegetable bits, and coffee grounds.
- Add garden waste such as leaves and grass clippings.
- Turn the compost regularly to speed up decomposition with microbes’ help.
- Meal Planning:
- Plan meals for the week to avoid buying extra food.
- Make shopping lists to prevent impulse buys.
- Store leftovers properly in the refrigerator.
- Portion Control:
- Serve smaller portions to reduce plate waste.
- Freeze leftovers for later use instead of throwing them away.
- Food Donation:
- Donate non-perishable foods to local charities or food banks.
- Check expiry dates before donating.
- Recycling:
- Recycle packaging from food products, including single-use plastics and cardboard boxes.
- Clean rinsed containers before placing them in the recycle bin.
- Storage Solutions:
- Use airtight containers to extend the shelf life of perishable items.
- Label and date items in the fridge and cupboards to use older products first.
- Creative Cooking:
- Use overripe fruits for smoothies or baking.
- Turn vegetable scraps into soup broth or sauces.
- Educating Family Members:
- Teach family members about proper waste prevention techniques.
– Involve children in sorting recyclables and composting activities.
- Teach family members about proper waste prevention techniques.
- Using Technology:
– Apps can help track expiry dates and suggest recipes using soon-to-expire items.
- Garden Waste Management:
– Compost garden clippings alongside kitchen scraps for richer compost material.
Reducing food losses at home helps conserve resources and minimises carbon dioxide emissions from decomposing waste in landfills, addressing issues like plastic pollution and malnutrition globally.
2. Through initiatives and campaigns
Initiatives and campaigns play a big role in reducing food waste. They encourage communities to adopt better practices.
- Public Awareness Campaigns:
- Educate people on the impact of food waste.
- Examples include Love Food Hate Waste in the UK.
- Use social media to spread tips on reducing waste.
- Food Donation Programmes:
- Redirect surplus food to people in need.
- Partnerships between supermarkets and charities ensure minimal waste.
- Helps combat global hunger by using excess food.
- Community Composting Projects:
- Set up local composting bins or sites.
- Residents can bring their kitchen scraps.
- Compost can be used for community gardens, promoting recycling.
- Government Initiatives:
- Implement policies that support reduction efforts.
- Provide grants for businesses aiming at zero waste goals.
- Introduce regulations to curb excessive waste at different stages of the supply chain.
- Innovative Technology Solutions:
- Apps like Too Good To Go connect consumers with unsold food from restaurants.
- Businesses use smart inventory systems to manage stock efficiently and reduce spoilage.
- Sensors in bins track the amount of wasted food, offering data for improvements.
- School Education Programmes:
Teach children about sustainable practices early on.
Encourage projects such as school gardens and composting lessons.
Promote habits that reduce future household food waste.
- Corporate Responsibility Pledges:
Companies commit to reducing their carbon footprint by lessening food losses during production.
Adopt practices such as upcycling by-products into new products.
Report progress annually, showing transparency and commitment.
- Festivals and Events:
Host events focused on sustainability, showcasing ways to reuse leftovers creatively.
Partner with chefs who demonstrate cooking techniques using whole foods, cutting down on wastage.
Highlight successful case studies from other regions.
These steps help manage food losses, conserve resources, and lessen environmental impacts effectively.
Government support and strategies
Governments play a crucial role in managing food waste. They can create policies that encourage businesses and homes to reduce wasted food. For example, laws can be made to keep food from being incinerated or put into landfills.
Many governments support composting and recycling programs. These initiatives help turn leftover food into useful products like compost for farming. By promoting waste hierarchy practices, governments aim to conserve resources and cut carbon dioxide emissions from rotting food in landfills.
Impact of Covid-19 on household food waste.
During the Covid-19 pandemic, household food waste saw a significant rise. Lockdowns led to panic buying and stockpiling, causing many households to buy more than needed. This behaviour resulted in increased food losses as perishable items spoiled before use.
Moreover, disruptions in the food supply chain added to this problem. Restaurants and schools closed for extended periods, leading families to cook more at home without proper meal planning skills.
This situation contributed further to food wasted as people struggled with managing larger quantities of groceries efficiently.
Conclusion
Sustainable food waste management helps protect our planet. It involves reducing, reusing, and recycling food waste. Simple actions like composting at home make a big difference. Government initiatives also play a key role in supporting these efforts.
Reducing food waste saves money and resources. Think about how you can start managing your own food waste better today! By doing so, you help create a healthier environment for everyone.
FAQs
1. What is food waste management?
Food waste management involves the process of handling food losses and food waste to reduce environmental impact.
2. Why is sustainable food waste management important?
Sustainable management reduces carbon dioxide emissions, promotes environmental justice, and ensures food safety throughout its life cycle.
3. How does recycling help in managing food waste?
Recycling helps by turning wasted or combusted materials into useful products, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
4. What role does the UK play in addressing food loss and wasted resources?
The UK focuses on synergies between different sectors like agriculture and food service to manage and recycle waste efficiently.
5. Can proper management of food waste benefit communities?
Yes, it can create synergies that improve local environments and support community health through better practices in recycling and reduced carbon emissions.
Discover more from IPPTS Depackaging Equipment Insights
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.